
PPT Erikson’s Theory Generativity versus Stagnation PowerPoint
Generativity Versus Stagnation: An Elaboration of Erikson's Adult Stage of Human Development Authors: Charles L. Slater California State University, Long Beach Abstract Erik Erikson's theory of.

PPT Erik Erikson and Life Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free
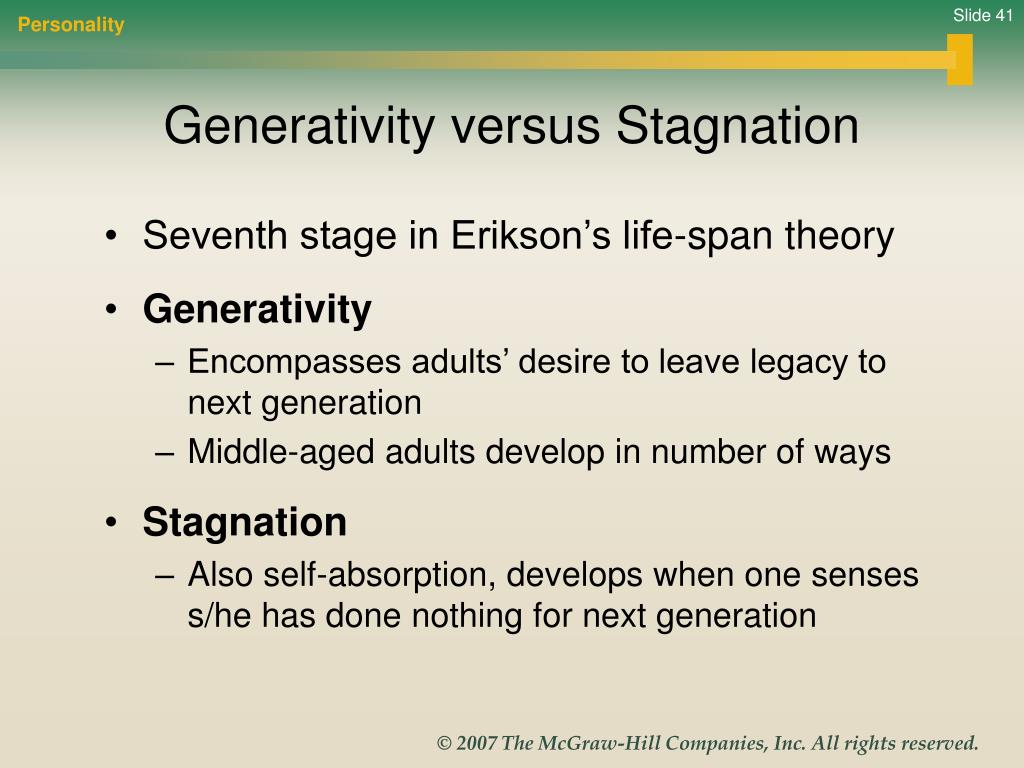
One broad category of developmental outcomes is generativity vs. stagnation. Erik Erikson developed the concept of generativity versus stagnation to describe the psychosocial development of middle adulthood. Between ages 40 and 65, this period is characterized by the conflict between generativity (nurturing the next generation) and stagnation.

Generativity vs Stagnation YouTube
Generativity vs. stagnation is the seventh stage of Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development. This stage takes place during middle adulthood, between the approximate ages of 40 and 65. It comes before the eighth and final stage of development in Erikson's theory, which is integrity vs. despair . During this stage, middle-aged adults.

Generativity vs. Stagnation Navigating Your Psychosocial Development
Generativity vs. stagnation is the seventh crisis a person experiences throughout social development. It follows the crisis of intimacy vs. isolation. People who successfully move through the sixth stage have a community that brings them joy. This could include a spouse, group of friends, family unit, etc. Generativity vs. Stagnation Age
PPT LIFESPAN DEVELOPMENT PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
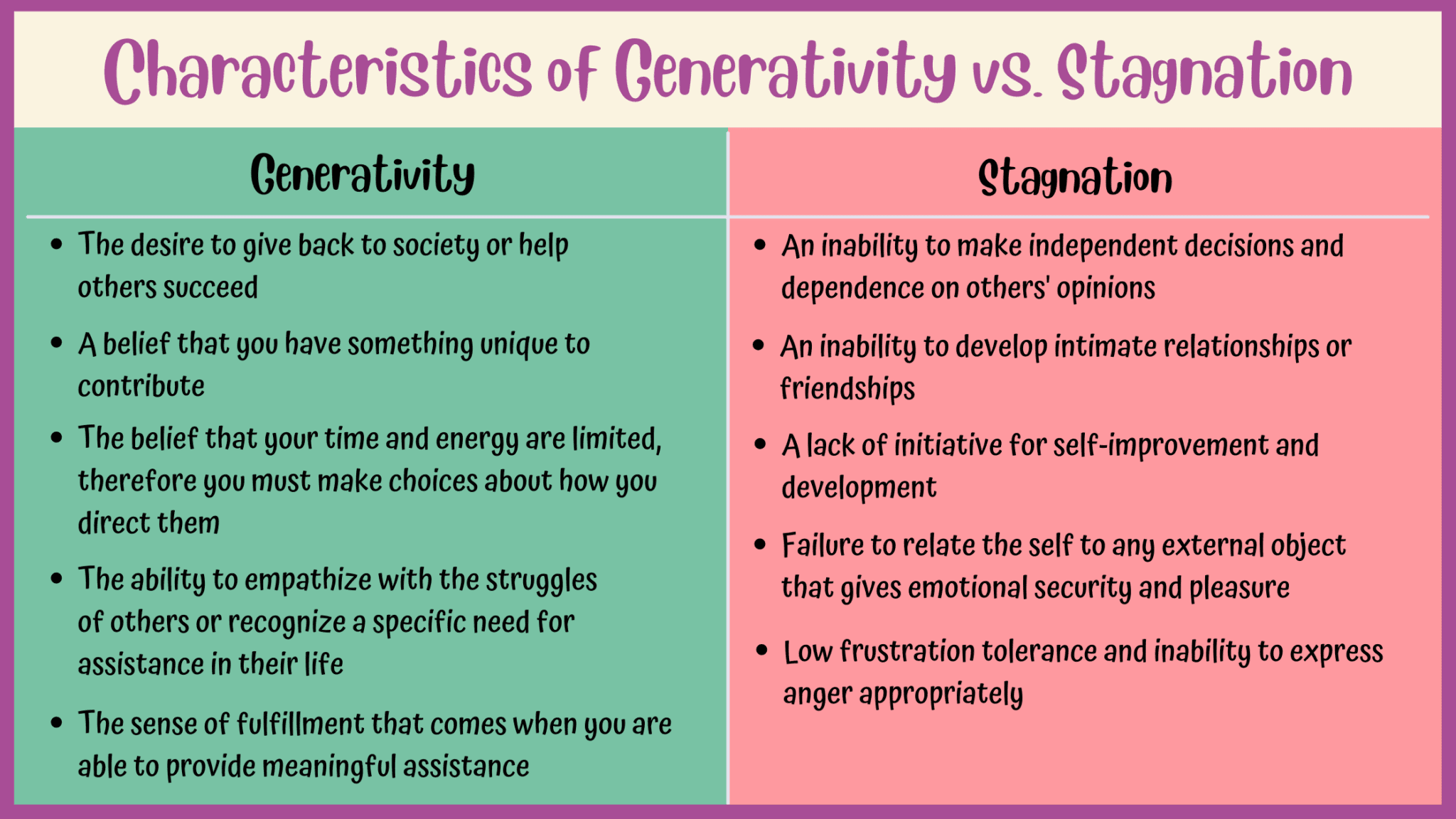
In Erikson's view, generativity involves a desire to give back to society, whether through raising children, mentoring others, contributing to one's community, or pursuing a fulfilling career. On the other hand, stagnation is the sense of not making progress in life.

Generativity Why Care? — Generativity
What's generativity vs. stagnation? It's a step closer to your goals By Madeline Miles July 18, 2022 - 17 min read Share this article Jump to section Breaking down generativity and stagnation What does generativity vs. stagnation look like? The effects of generativity vs. stagnation 6 ways to inspire generativity and reduce stagnation

PPT Erik Erikson PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2445188
The Wall of Stagnation In many ways, stagnation is the opposite of generativity. With stagnation, you don't consider the interests or needs of others. In fact, you might describe your actions as selfish. There is no concern for doing meaningful work or being productive.

PPT Erik Erikson PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2676858
"Generativity" refers to a sense of productivity, contribution, and positively impacting the world. It may involve nurturing and guiding the next generation, mentoring others, or contributing to society through meaningful work or community involvement. On the other hand, "stagnation" represents feeling stuck, unproductive, and lacking purpose.

PPT Erikson's theory Psychosocial Theory of Development PowerPoint
Psychosocial Development Guide Erikson's Stages of Development A Closer Look at the Eight Psychosocial Stages By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Updated on August 03, 2022 Reviewed by David Susman, PhD Table of Contents View All Overview of Erikson's Stages of Development Trust vs. Mistrust Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt Initiative vs. Guilt
PPT Adolescence PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5163308
This page titled 8.12: Erikson- Generativity vs Stagnation is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Martha Lally and Suzanne Valentine-French via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/generativity-versus-stagnation-2795734_final-8464025771694e779bc84be73010b6f2.jpg)
Generativity vs. Stagnation in Psychosocial Development
Go to: Abstract Erikson's (1950) model of adult psychosocial development outlines the significance of successful involvement within one's relationships, work, and community for healthy aging. He theorized that the consequences of not meeting developmental challenges included stagnation and emotional despair.
A Look at Generativity vs. Stagnation
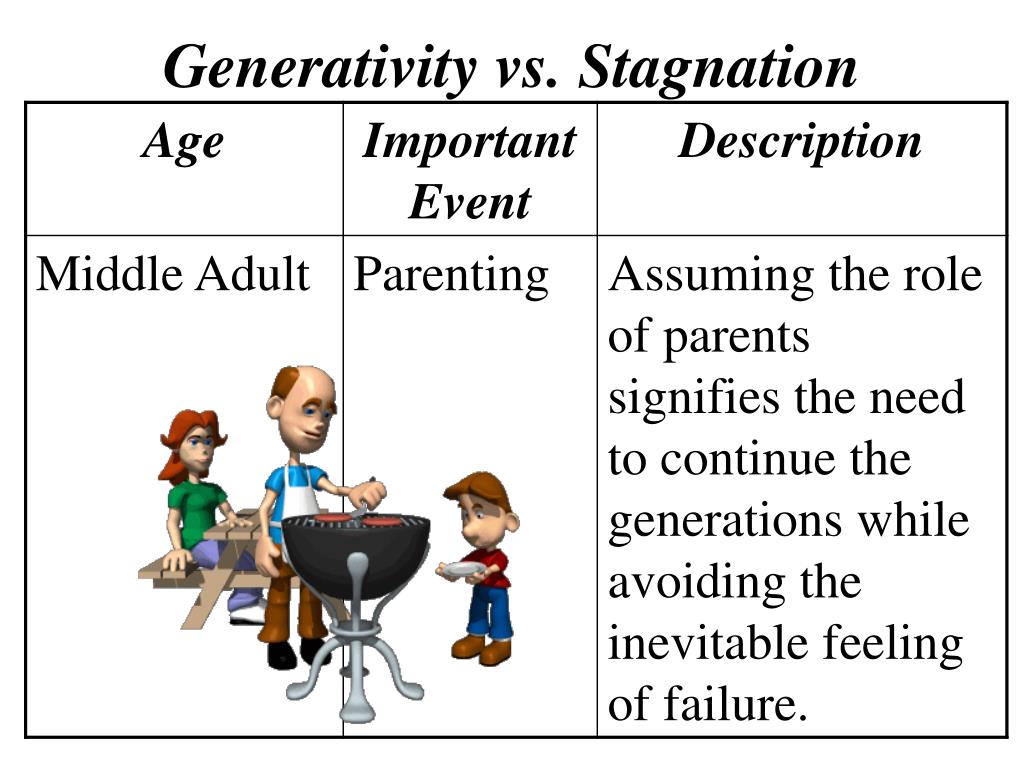
This stage includes the generation of new beings, new products, and new ideas, as well as self-generation concerned with further identity development. Erikson believed that the stage of generativity, during which one established a family and career, was the longest of all the stages.

PPT Emotional and Social Development in Middle Adulthood PowerPoint
This period of introspection is known as generativity vs. stagnation, the seventh stage of Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development. During this stage, individuals between the ages of 40 and 65 face the challenge of creating a meaningful impact on the world and future generations or risk feeling unfulfilled and stagnant.

PPT Erikson’s 8 Stages of psychosocial development PowerPoint
The seventh recovery stage, purpose versus passivity, parallels Erikson's generativity versus stagnation stage and involves finding a life strategy for living well with a psychiatric disability despite sometimes disabling symptoms. Individuals use their repertoire of coping skills learned throughout the recovery process and spend their energy.

Psychosocial development, Developmental theories, Emotional development
Generativity is psychologist Erik H. Erikson's term for the primary developmental task of the seventh stage of the life cycle - caring for and contributing to the life of the next generation. The developmental challenge of adults in their middle years is to be procreative, productive, and creative and to overcome a pervading mood of self.

Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Developmetn
Stage 7: Generativity vs. Stagnation . Erikson's seventh level of psychosocial development occurs during middle age—between 40 to 65 years of age. The crisis at this stage is generativity vs. stagnation. Generativity is a person's way of "leaving a mark" on the world by giving back to society. This can include mentoring the younger generation.